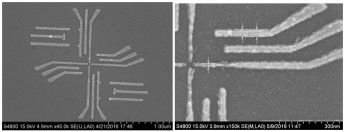
CSAR 62 is routinely used to produce innovative quantum devices at the TU Delft (Mr. Toivo Hensgens, TU-Delft, the Netherlands). For the structures shown below, a 72 nm layer of CSAR 62 was exposed to 100 kV and then developed with amyl acetate. By metal deposition (lift-off process), nano-sized aluminium gates could be realized on GaAs. These structures are suitable for the investigation of single electrons which can be captured electrostatically in the underlying semiconductor layer; an important prerequisite for the realisation of quantum processors.
Fig. 1: Al-gates on GaAs, produced through a subsequent metallisation of CSAR 62 lift-off architectures (layer thickness CSAR 62: 72 nm, 100 kV VISTEC – e-beam writer EBPG5000+ or EBPG5200). Line diameter: about 16 nm or 34 nm.
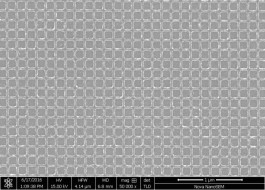
CSAR 62 is also highly suitable for the production of regular grid structures which can e.g. be used for the investigation of quantum effects with electrons (2D electron gas).
Fig. 2: Highly regular grid structure of CSAR 62 on GaAs, mesh diameter about 150 nm, line diameter 40 nm (working group of Mr. Toivo Hensgens, TU Delft, the Netherlands).